Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITB): Common Causes, Exercises & Treatment Options. Do You Have A Question? Speak To A Therapist Today. Call (24/7): 1300-003-777.
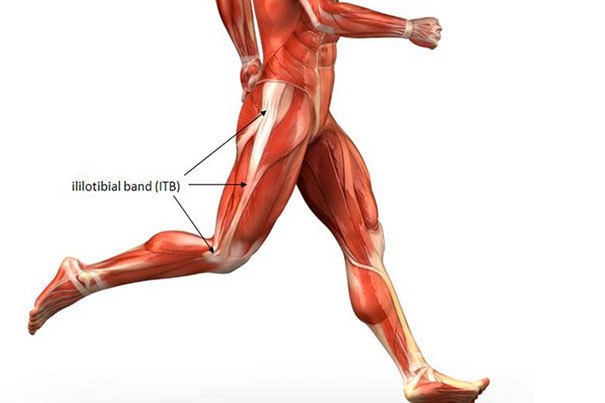
Iliotibial band syndrome (ITB) is also commonly referred to as iliotibial friction syndrome and is one of the most common causes of idiopathic knee pain in runners and recreational athletes. It’s an overuse or repetitive type injury. The ITB muscle originates at the proximal hip from the tendons of the tensor fascia latae and gluteus maximus muscles. It extends through the iliotibial tract along the lateral side of the thigh to cross the knee joint and insert at the femoral condyle of the tibia. It’s at this point that friction may occur during knee movement and therefore cause the characteristic painful symptoms of iliotibial band syndrome. It’s important to recognize that IT band syndrome does not just effect runners & athletes. Any person may experiencing ITB pain.
Causes Of Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome
Iliotibial band syndrome is caused by altered running biomechanics due to underlying muscular imbalance. Other contributing factors of iliotibial band friction include:
- Poor biomechanics (gait and running technique) that causes dysfunction within the foot, ankle, knees and hips.
- Weak supporting musculature including gluteals, hip flexors, quadriceps and core.
- Poor foot and arch stability such as over-pronation or flat feet.
- Inappropriate footwear.
- Sudden increase in exercise or activity load.
Symptoms Of ITB Muscle Pain
As with all musculoskeletal complaints there are varying degrees of severity and symptoms. Characteristic symptoms of iliotibial band syndrome may include:
- A sharp burning or uncomfortable sensation on the outside of the knee and/or thigh.
- Pain is particularly worsened during activity.
- There may be generalized swelling noted of the knee joint.
- Sensitivity and tenderness of the knee joint and lateral thigh upon palpation.
Management Of Iliotibial Band Injuries
Many clients who present to our clinic suffering from iliotibial band syndrome respond well to conservative management. Your treating practitioner will discuss with you the important findings from your examination as well as detail a tailored rehabilitation regime to assist your prompt recovery. This may include:
- Strategies to promptly reduce acute pain and associated iliotibial band inflammation.
- Exercises or activities to unload your iliotibial band.
- Restore normal lower kinetic chain (hip, knee, ankle) biomechanics and movement.
- Strengthen associated muscles to reduce the probability of injury recurrence.
Chiropractor Iliotibial Band Syndrome Research
- It has been conventional thinking that iliotibial band tightness concurrent with hip abductor weakness were significant contributors in the development of lower back pain. This study demonstrates that this theory is not always the case and further analysis into iliotibial band syndrome is warranted. Arab, A. (2010). The relationship between hip abductor muscle strength and iliotibial band tightness in individuals with low back pain. Chiropractic & Osteopathy, 18(1):
- Iliotibial band syndrome (ITB) is a common occurrence among physically active individuals that typically causes lateral knee discomfort. Successful treatment appears to include conservative measures such as reducing inflammation, strengthening, stretching, modification of neuromuscular control during gait and soft tissue therapy. Lavine, R. (2010). Iliotibial band friction syndrome. Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine, 3(1-4); 18 – 22.
Additional Information
If you wish to continue your reading about Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITB) please click here.
