Rotator Cuff Syndrome: Sports Chiropractor Discusses Causes, Symptoms & Treatment. Want To Speak To A Therapist? Call (24/7): 1300-003-777.
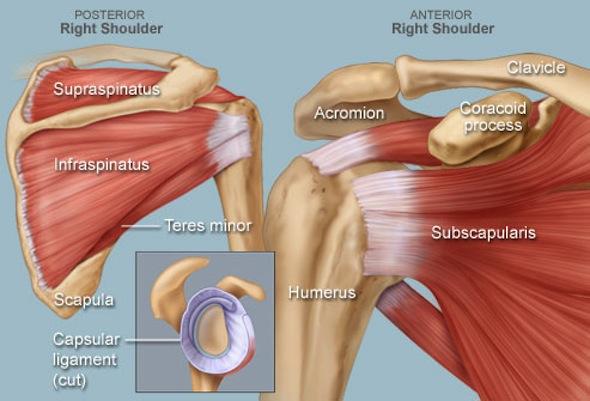
A rotator cuff tear is a tear in one or more of the four muscles that make up the rotator cuff of the shoulder girdle. These tears are a common shoulder condition that we frequently encounter in clinical practice. Rotator cuff injuries affect up to 30% of people during their lifetime. Males are more likely to suffer from rotator cuff tears and the condition can appear in all types of people ranging from athletes, physical workers, elderly as well as anyone from the wider population. The rotator cuff plays an important role for shoulder stability helping to keep your shoulder joint aligned as well as ensuring normal arm movement and mobility during regular activity.
Causes Of Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
There are four common ways that you may suffer from rotator cuff syndrome.
- Acute trauma & direct injury: Trauma may be the result of activities such as sports injuries, falls as well as lifting and lowering objects.
- Repetitive overuse: Continual or repetitive loading the shoulder may contribute to micro-tears.
- Age related degeneration: As we age soft tissue and connective tissues weaken which lead to an increased risk of injury.
- Associated conditions: You may sustain rotator cuff syndrome due to other shoulder complaints such as Supraspinatus injury, Labral tears, Bursitis, Shoulder instability or Shoulder impingement syndrome.
Signs & Symptoms Of Cuff Syndrome
Rotator cuff injury symptoms vary depending upon severity of your complaint. Symptoms which may indicate that you’re suffering from rotator cuff syndrome can include (but not limited to):
- Pain on the upper or outer shoulder region.
- Night pain that may contribute to difficulty sleeping or lying on the affected shoulder.
- Shoulder weakness during particular movements.
- A clicking or ‘popping’ type sensation in the shoulder in the presence or absence of pain.
- Swelling and associated skin changes.
How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a rotator cuff tear is a thorough process as it’s essential to locate the specific muscle that is injured. Your practitioner must rule out possible differential diagnoses before commencing treatment. A consultation with a therapist such as a Chiropractor or Physiotherapist may include the following assessment:
- Review of medical history: This is important as your practitioner needs to understand the exact mechanism of injury, location of pain, quality of pain and any potential aggravating factors.
- Physical examination: An assessment may include palpation of the shoulder region, muscle testing to observe for weakness or asymmetries, range of motion of the shoulder girdle as well as various orthopaedic and neurological tests if required.
- Referral for imaging may be clinically indicated: In particular cases your treating practitioner may suggest referral to your general practitioner for further analysis such as X-ray, Ultrasound, MRI or CT.
Rotator Cuff Treatment
Conservative management such as Chiropractic & Physiotherapy are a fantastic option for treating these injuries. Depending upon severity of your injury you may expect rehabilitation time between weeks to several months. Other helpful management strategies may include:
- Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain and dysfunction.
- Resting the injured area to assist with reducing inflammation, overall pain and improving general function.
- Other anti-inflammatory measures such as ice application to the injured area, anti-inflammatory medication as well as dietary or nutritional changes.
Chiropractic & Physiotherapy
- Strategies to assist with reducing inflammation such as ice/heat, ultrasound application, laser and shockwave therapy.
- Soft tissue therapy to assist with injury healing and reducing pain as promptly as possible.
- Exercises to improve shoulder range of motion and therefore allow for treatment progression towards strengthening based exercises.
Corticosteroid Injections
Surgical Intervention
Chiropractor Rotator Cuff Syndrome Research
- Conservative treatment may lead to satisfactory results when it’s administered to individuals who have well preserved shoulder range of motion and strength. If more severe cases, alternative treatment methods should be considered and referred for appropriately. Itoi, E. (1992). Conservative treatment of rotator cuff tears. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research, 165 – 173.
- Statistically significant improvements were obtained in shoulder range of motion, pain and general function from conservative management. Baydar, M. (2009). The efficacy of conservative treatment in patients with full-thickness rotator cuff tears. Rheumatology International, 29(6); 623 – 628.
Additional Information
If you’re seeking additional information regarding Rotator Cuff Syndrome please visit the Mayo Clinic.
